Shell
which vs type🔖
which🔖
- finds executable in your
$PATH - lives in /usr/bin/which
type🔖
- if used with the
-aflag ("all"), it determines if the command is an alias, function, built-in command, cached executable (hashed) or binary in$PATH, etc - shell builtin
Example output when used with the -a flag
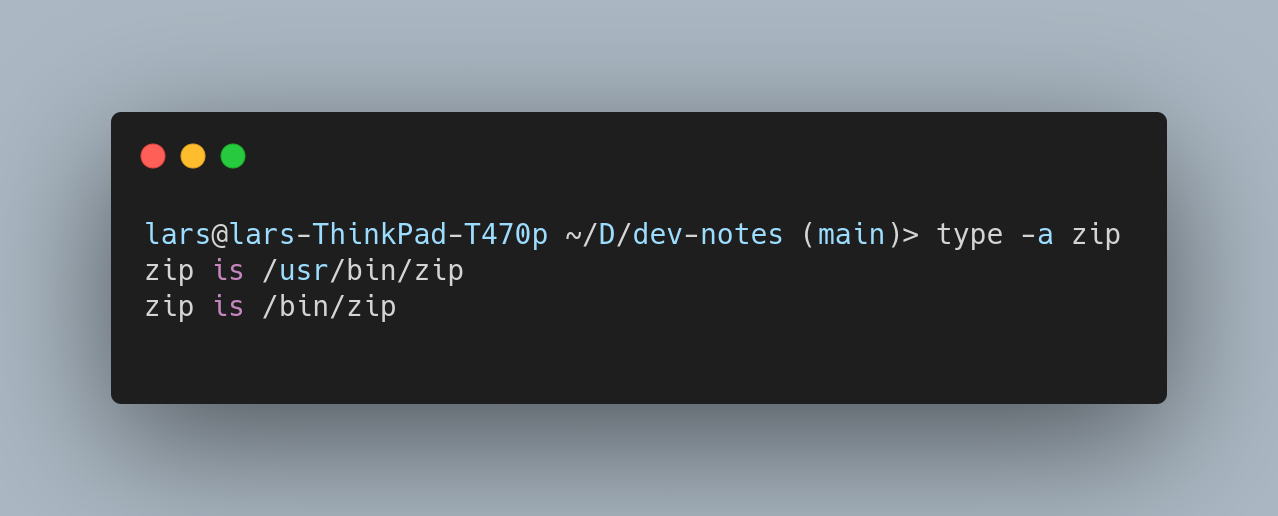
Other command options are:
-tsingle word output for the type, e.g. alias, buildin, function etc-ppath to the disk file
Users🔖
Find user name belonging to user ID
id -un <ID>
ssh🔖
Connect to remote host via ssh with public key authentication. If no public/private key pair exists yet run first.
ssh-keygen
Then copy the public key to the remote machine
ssh-copy-id <login user name>@<remote host name>
alias🔖
Add to /home/<user>/.ssh/config
Host <your alias>
HostName <full remote host name>
User <login user name>
In combination with public key authentication you can now login to the remote machine without being prompted for a password with
ssh <your alias>
control path and master🔖
Re-use an existing connection to server you already have logged into.
To enable for all hosts add the following to /home/<user>/.ssh/config
host *
controlmaster auto
controlpath ~/.ssh/control-%h-%p-%r
This will put the shared sockets in the ~/.ssh directory.
- %h - Host
- %p - Port
- %r - Remote login username
Host, port and login username substitutions ensure unique shared connections.
Resources🔖
dig🔖
Short for Get Domain Details.
Possible types
| Query type | Output | Function |
|---|---|---|
| A | IPv4 address record | Returns an IPv4 address. |
| AAAA | IPv6 address record | Returns an IPv6 address. |
| SOA | A zone of authority record | Returns authoritative information about a DNS zone. |
| CNAME | Canonical name record | Returns an alias for the target domain and all subsequent aliases. |
| MX | Mail exchange record Returns a list of message transfer agents assigned to the target domain. | |
| PTR | Pointer record | Returns a canonical name. Most commonly used for reverse DNS look-ups. |
| NS | Name server record | Returns an authoritative name server for the target domain. |
Resources🔖
Example on how to solve DNS issues
find🔖
General form
find (starting directory) (matching criteria and actions)
To find all files under the current directory of type plain text with the file extension .ts
find . -type f -name "*.ts"
Option type🔖
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| f | plain text |
| d | directory |
Option mtime🔖
The file was modified x days ago. You can use + and - operators to narrow down your search.
Find csv files last modified more than 5 days ago
find . -type f -mtime +5 "*.csv"
Find csv files last modified last week
find . -type f -mtime -7 "*.csv"
Action exec🔖
You can execute a command that will be applied to all found files, like removing them.
don't forget the backslash semicolon!
Commands you want to execute must end with \;
find . -type f -name "*.ts" -exec rm -rf {} \;
Action ok🔖
If you want to confirm the action before the command will be applied use -ok instead of -exec
find . -type f -name "*.ts" -ok rm -rf {} \;
This will prompt before actually executing the command
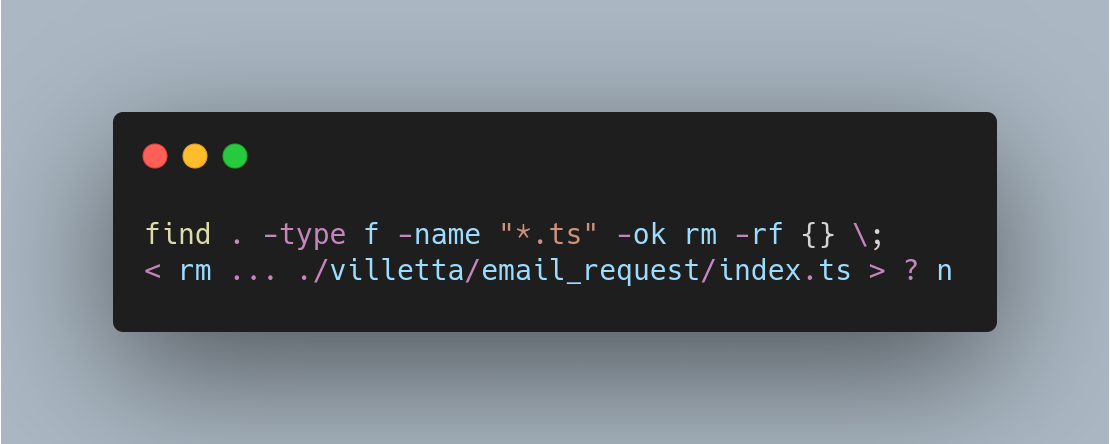
Use y or yes to confirm, n or no to abort.